MonoNeRF (ICML 2023) 這篇論文探索了一個重要的問題:如何在缺乏真實相機姿態(camera poses)標註的情況下,從普通的單眼視角影片(monocular videos)中學習可泛化的神經輻射場(NeRFs)。本篇筆記旨在整理該研究提出的解決方案,內容涵蓋其核心的自動編碼器(autoencoder)架構、用於估計相對相機姿態與單眼深度的編碼器、基於多平面影像(Multiplane Images)的 NeRF 解碼器,以及實現自監督學習所依賴的自動尺度校準(auto-scale calibration)等關鍵技術細節。
- Link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.07181
- Conference: ICML 2023
Introduction#
- Problem Setting
- 在靜態場景中移動的 large-scale monocular videos 上進⾏訓練,⽽無需任何深度和 camera pose 的 ground-truth。
- 以 self-supervision 的方式,通過 autoencoder,從 monocular videos 中學習可泛化的 NeRF 表示。(無需相機姿態和深度的 ground-truth)
- Challenges
- NeRF 在重建場景過程中需要有 ground-truth camera pose。
- 大多數情況下僅適用於一個場景。
- Key Insight
- 在現實世界中,影片通常伴隨著攝影機緩慢變化(連續性)。
- 因此本篇的主要方法為根據輸入幀,預測渲染幀。
- Contribution
- 第一個在沒有 ground-truth camera pose 的情況下,在 large-scale dataset 上學習 NeRF 的工作。
- 可以從單一 RGB 影像進行多種下游任務:
- 單目深度估計。
- 相機姿態估計。
- Novel View Synthesis
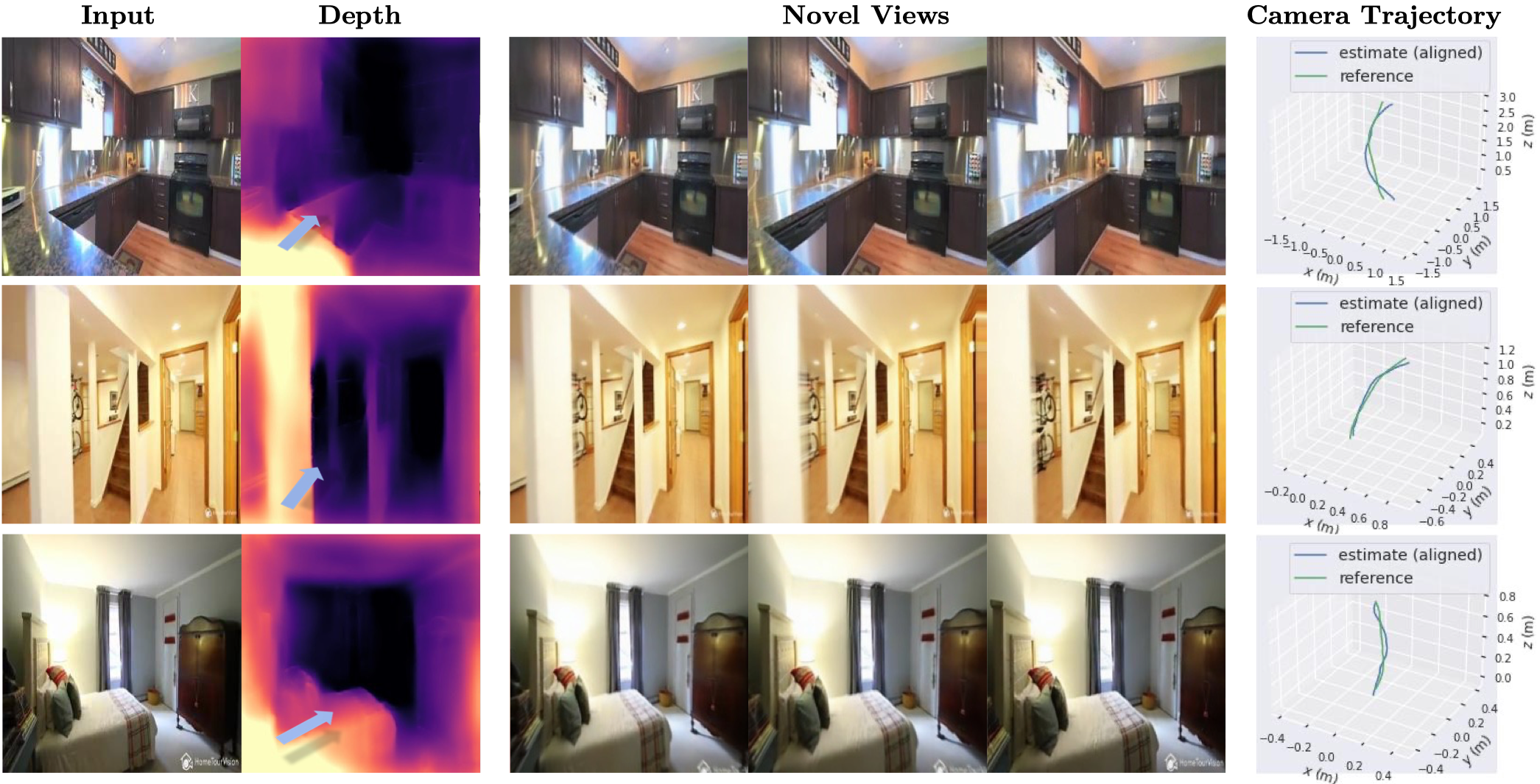
Methods#
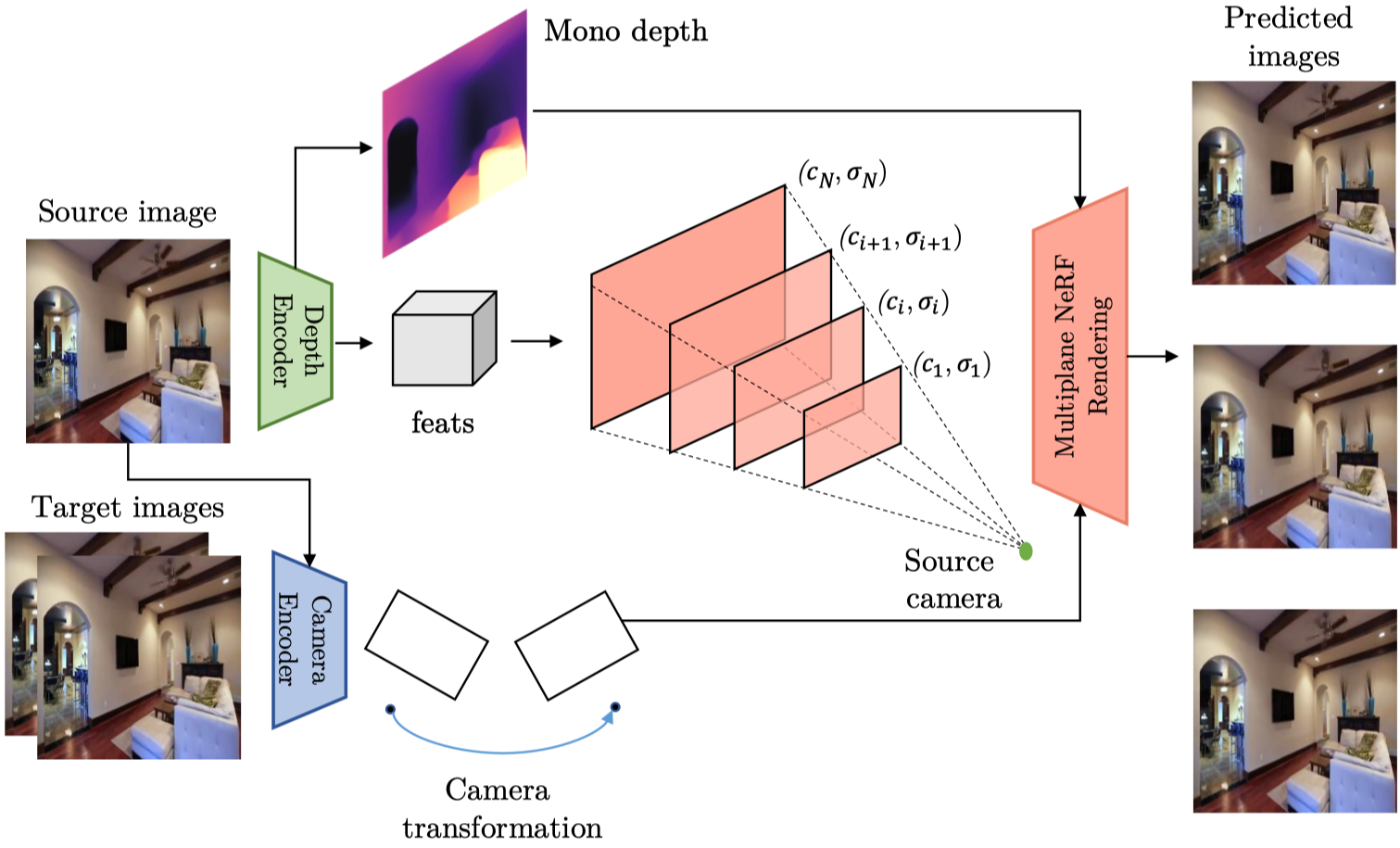
Overview#
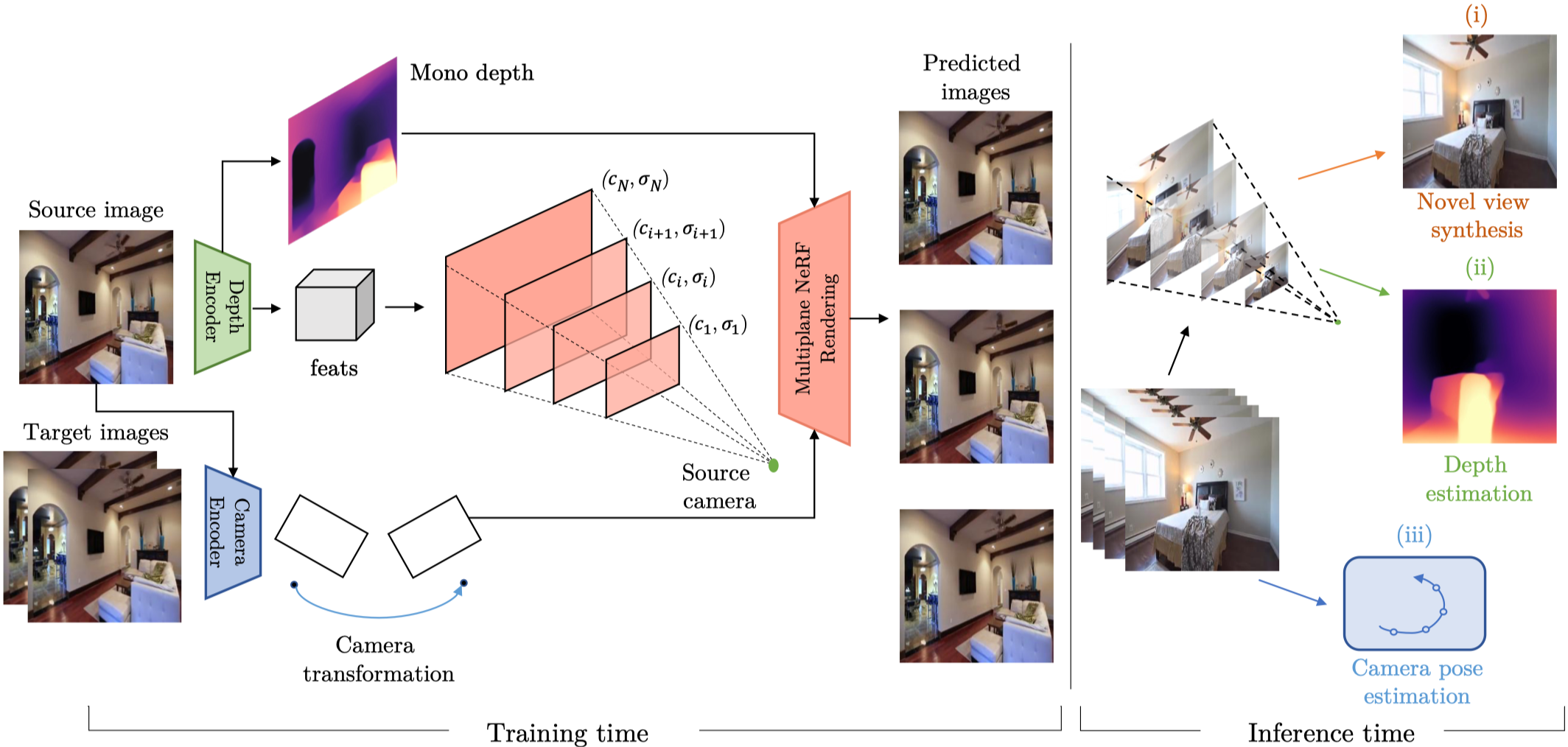
- 使用 Camera Encoder ,根據預測兩幀之間的相機姿態變化(旋轉與平移矩陣)。
- 使用 Depth Encoder,預測 monocular depth,同時中間的 feature 會被應用到 multi-plane 上,並以不同視差等級的平面結合。
- 透過 Multiplane NeRF 渲染影像。
在推理過程中,可以應用於不同子任務:
- Novel View Synthetic
- Depth Estimation
- Camera Pose Estimation
Camera Pose Encoder#
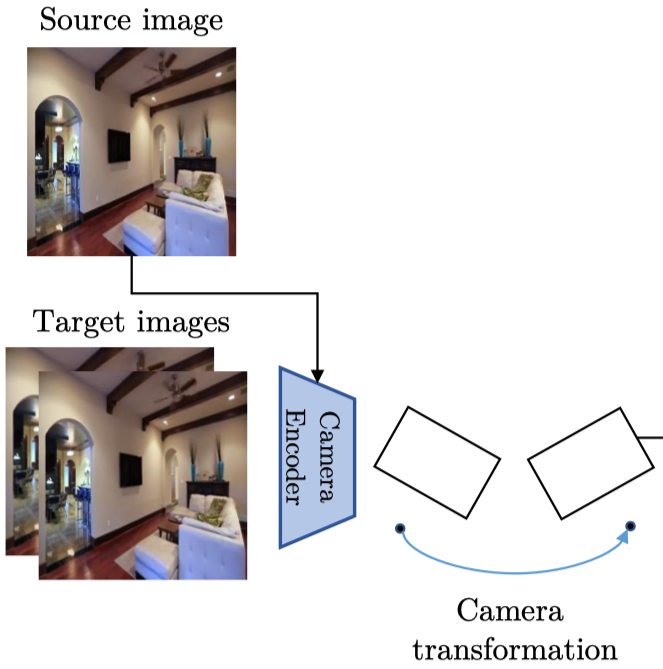
目的:
- 預測兩個 input frame 之間的相對相機變換。
- 給定一個 source frame 與一個 target frame,他會計算 source camera 到 target camera 的旋轉與平移矩陣。
- 有了所有 target images 的估計相機姿態,就可以建立相機軌跡,然後用於 decoder 中的 target view synthesis。
訓練期間:
使用輸入序列的中間影格作為 source view image,並將前後其他的影格作為 target image。
實作:
- 使用 ResNet 架構設計 Camera Pose Encoder。
- 將兩個幀作為輸入(沿著通道維度將兩個 frame 堆疊成 6-dim)。
- 輸出一個 6-dim vector (包含 3D rotation 與 translation)。
Monocular Depth Encoder#
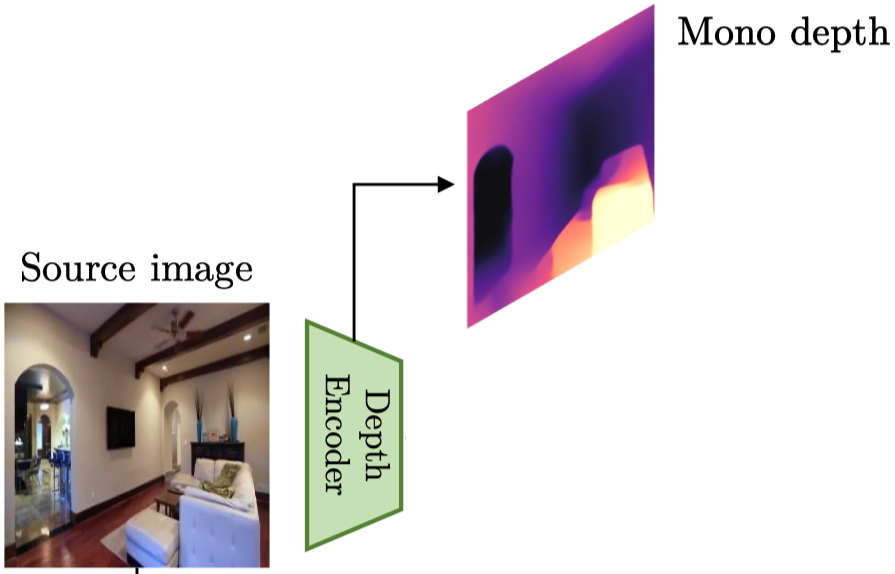
目的:
- 從每個單一輸入幀估計 monocular depth。
- 輸出的 monocular depth map 用作中間表示,來指導 Multiplane NeRF 的建構。
實作:
- 採用 MnasNet 的架構。
- 通過提取不同解析度尺度的 feature map 來預測 depth map。
- NOTE: 原始的輸出是視差圖 (disparity map),需要轉換成 depth map。
Multiplane NeRF based Decoder#
Multiplane Images#
一個影像會被表示成一組平行的平面 RGB-$\alpha$, $\{(c_i, \alpha_i) \}^D_{i=1}$。$D$ 表示平面的數量。
每個平面對應到一個特定的 disparity value $d_i$ (深度的倒數)。 $d_i$ 是從預定義的範圍 $[d_{\text{min}}, d_{\text{max}}]$ 中均勻採樣得到的。
給定 target to source view 的旋轉與平移矩陣,與 source 與 target view 的 intrinsics matrix $K_s, K_t$,我們能通過下面的方法得到 target-view image $\mathbf{\hat{I}}_t$ 與 disparity map $\mathbf{\hat{D}}_s$:
將 $i$-th plane 從 target 變形至 source view 的 warping function 可以表示成 Eq. \eqref{eq:3}:
$$ \begin{align*} \begin{bmatrix} u_s \\ v_s \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} &\sim K_s (R - tn^Td_i)(K_t)^{-1} \begin{bmatrix} u_t \\ v_t \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} \tag{3} \label{eq:3} \end{align*} $$符號 描述 $n$ The norm vector of the $i$-th plane. $[ u, v ]$ The coordinates in view. 通過將 source viewpoint 的每層變形至 target viewpoint 即可得到 target view 的 MPI 表示。
$$ \begin{align*} c_i'(u_t, v_t) &= c_i(u_s, v_s) & \alpha_i'(u_t, v_t) &= \alpha_i(u_s, v_s) \tag{4} \end{align*} $$最後在通過 Stereo Magnification 的合成方法得到 RGB image 和 disparity map:
$$ \begin{align*} \mathbf{\hat{I}}_s &= \sum_{i=1}^{D} \left( c_i \alpha'_i \prod_{j=i+1}^{D} (1 - \alpha_j) \right) \\ \mathbf{\hat{D}}_s &= \sum_{i=1}^{D} \left( d_i \alpha_i \prod_{j=i+1}^{D} (1 - \alpha_j) \right) \tag{5} \label{eq:5} \end{align*} $$$$ \begin{align*} \mathbf{\hat{I}}_t &= \sum_{i=1}^{D} \left( c_i' \alpha_i' \prod_{j=i+1}^{D} (1 - \alpha_j') \right) \\ \mathbf{\hat{D}}_t &= \sum_{i=1}^{D} \left( d_i \alpha_i' \prod_{j=i+1}^{D} (1 - \alpha_j') \right) \tag{6} \end{align*} $$
Multiplane NeRF#
作者通過引入 NeRF 來推廣 Multiplane Images。
MPI 是由多個平面的 RGB-$\alpha$ 組成,這樣所產生的深度會是稀疏且離散的。
與之不同,Multiplane NeRF 可以在任意深度預測 RGB-$\alpha$ image 以達成連續的 3D 場景表示。
$i$-th 平面可以表示成 Eq. \eqref{eq:7}:
$$ \begin{align*} \{c_i, \alpha_i\} &= \mathcal{F}_{\text{mpi}}(\mathbf{I}_s, \text{PE}(d_i)) \tag{7} \label{eq:7} \end{align*} $$NOTE: 對於 source image,只需要執行一次 depth encoder 提取 image feature。
重建步驟:
- 給定估計的相機軌跡。
- 通過 Eq. \eqref{eq:3} 的 warping function 獲得 target view 上的 RGB 與 density。
- 將 Eq.\eqref{eq:5} 中的 $\alpha$ 改成 density 。
- 使用 NeRF 的 volume rendering 獲取圖像與 disparity map。
與普通的 NeRF 相比,具有兩個優點:
- 可以從單一影像中建立 frustum。
- 更好的泛化能力,允許對 large-scale data 進行訓練。
Supervision with RGB#
在訓練期間, autoencoder 會通過比較渲染的 target view 與 ground-truth 來監督。然而,由於沒有使用 depth map 與 camera pose 的 ground-truth,因此直接這樣進行監督會導致不好的結果。
因此本篇另外提出兩個關鍵技術貢獻來實現深度和相機姿態的分離:
- Auto-scale Calibration
- New Loss Function
Auto Scale Calibration#
由於 Multiplane NeRF 是基於單一的影像建構的,因此可能導致比例模糊的問題。
在以往的方法中,會使用 SfM 來估計 camera pose 和 depth map (兩者具有相同的比例),並通過比較 SfM 的深度和 Multiplane NeRF 渲染的深度圖來校正相機姿態。然而這樣的方法非常耗時,且不總是成功(SfM 的原因)。
本篇方法使用 Autoencoder 來估計相機姿態與 disparity map,以克服 SfM 的限制。但這樣方法所生成的 camera pose, disparity map, rendered disparity map 都不是相同的尺度。
作者使用下面的方法進行校準:
Depth Consistency
首先使用 L1 Loss 來鼓勵 rendered disparity map 與 predicted disparity map 保持一致,這樣可以將兩者的深度對齊。
實作上是先將 disparity 轉換成 depth,接著才算 L1 Loss。
$$ \begin{align*} \mathcal{L}_{\text{consist}} &= \frac{1}{HW} \sum \left| \frac{1}{\mathbf{D}_s} - \frac{1}{\hat{\mathbf{D}}_s} \right|_1 \tag{8} \end{align*} $$Reprojection Consistency
給定 predicted disparity map, camera transformation 與 camera intrinsic,將 $\mathbf{I}_t$ 的像素重新投影回 $\mathbf{I}_s$。並在合成的 source image 與原始的 source image 之間使用 photometric reprojection loss。
Loss Function#
RGB L1 Loss
$$ \begin{align*} \mathcal{L}_{\text{L1}} &= \frac{1}{HW} \sum |\mathbf{\hat{I}}_t - \mathbf{I}_t| \tag{10} \end{align*} $$RGB SSIM Loss
$$ \begin{align*} \mathcal{L}_{\text{SSIM}} &= 1 - \text{SSIM}(\mathbf{\hat{I}}_t, \mathbf{I}_t) \tag{11} \end{align*} $$Edge-aware disparity map smoothness loss
$$ \begin{align*} \mathcal{L}_{\text{smooth}} = \left| \partial_x \frac{\mathbf{\hat{D}}_s}{\mathbf{\bar{D}}_s} \right| \exp ^{- \left| \partial_x \mathbf{I} \right| } + \left| \partial_y \frac{\mathbf{\hat{D}}_s}{\mathbf{\bar{D}}_s} \right| \exp^{ -\left| \partial_y \mathbf{I} \right| } \tag{12} \end{align*} $$Total Loss
$$ \begin{align*} \mathcal{L} = \lambda_{\text{L1}} \mathcal{L}_{\text{L1}} + \lambda_{\text{SSIM}} \mathcal{L}_{\text{SSIM}} + \lambda_{\text{smooth}} \mathcal{L}_{\text{smooth}} \\ + \lambda_{\text{consist}} \mathcal{L}_{\text{consist}} + \lambda_{\text{reproj}} \mathcal{L}_{\text{reproj}} \tag{13} \end{align*} $$
Experiments#
Implementation Details#
- 輸入影像縮放至 256x256。
- 訓練期間隨機採樣一組 3 frames 的序列。每個 frame 之間的間隔為 5,以確保相機的運動量足夠大。
- Multi-plane 的數量 $D$ 設置為 64。
- Camera frustum 的範圍設置為 $[0.2, 20]$。
- Batch size 為 4。
Experimental Settings#
- 作者對 MonoNeRF 進行三種任務的比較:
- Monocular Depth Estimation
- Camera Pose Estimation
- Single Image Novel view synthesis
- 在室內場景進行評估。
- 作者認為室內場景具有更多結構差異。
- 更常用於同時評估上述三種任務。
Depth Estimation#
Dataset
- ScanNet
- NYU-depth V2
作者使用 MonoNeRF 的 rendered depth map 作為預測結果。
- 渲染的 depth map 會比 Estimator 直接預測的平滑。
Metrics
- Absolute depth error (abs err)
- Absolute relative depth error (abs rel)
- Absolute log depth error (log10)
- Squared relative error(sq rel)
- RMSE
- Inlier-ratio with threshold (σ)
Baseline
- The depth supervision model
- MVDepthNet
- GPMVS
- DPSNet
- Atlas
- Depth in the Wild
- MegaDepth
- 3DKenBurns
- MiDaS
- The RGB supervision model with camera pose
- MPI
- MINE
- RGB-only
- MonodepthV2
- Manydepth
- MovingIndoor
- The depth supervision model
ScanNet
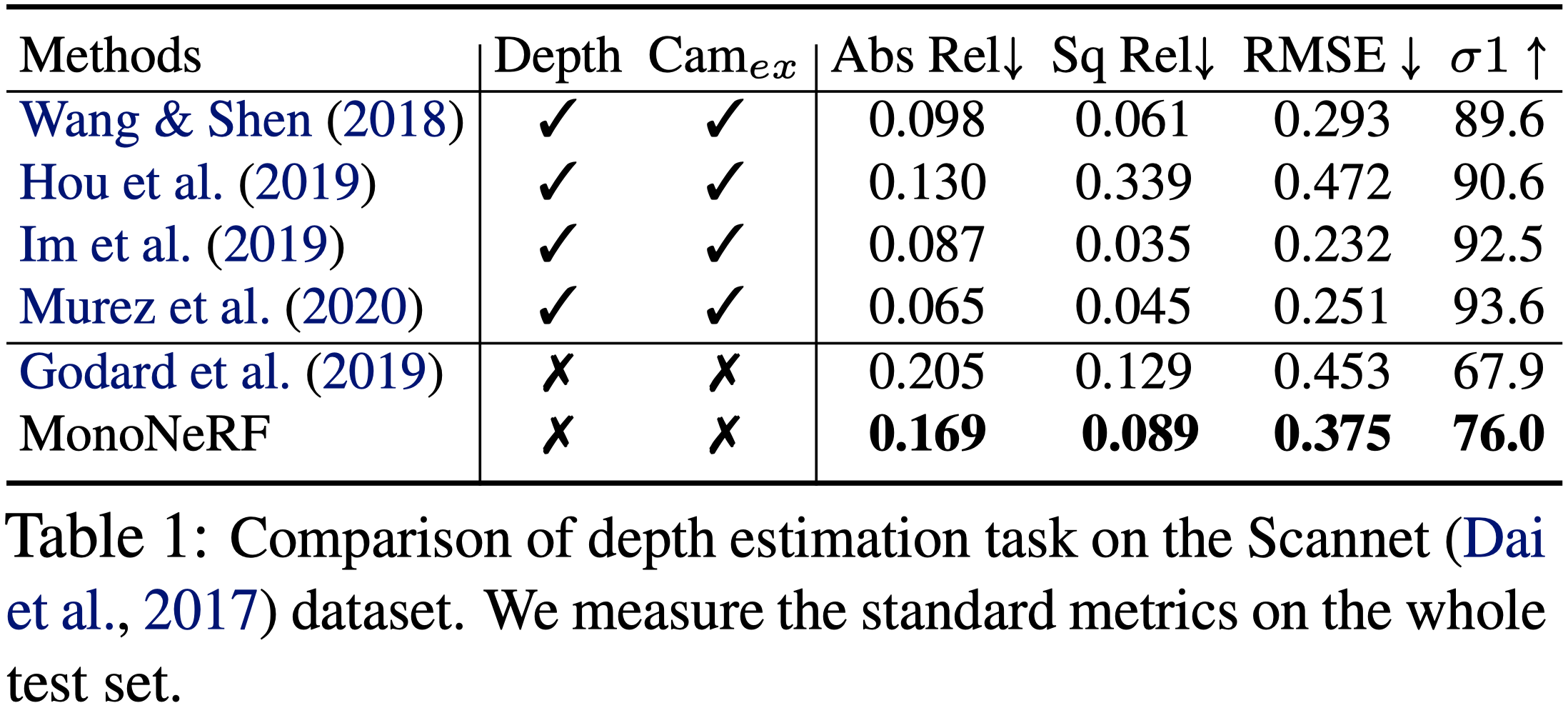
- 與 MVS—based 的方法相比,本篇方法無需任何的深度或相機姿態 ground-truth,就可以獲得不錯的效果。
- 與 RGB-only 的方法相比,本篇可以超過以往的方法。
NYU Depth V2
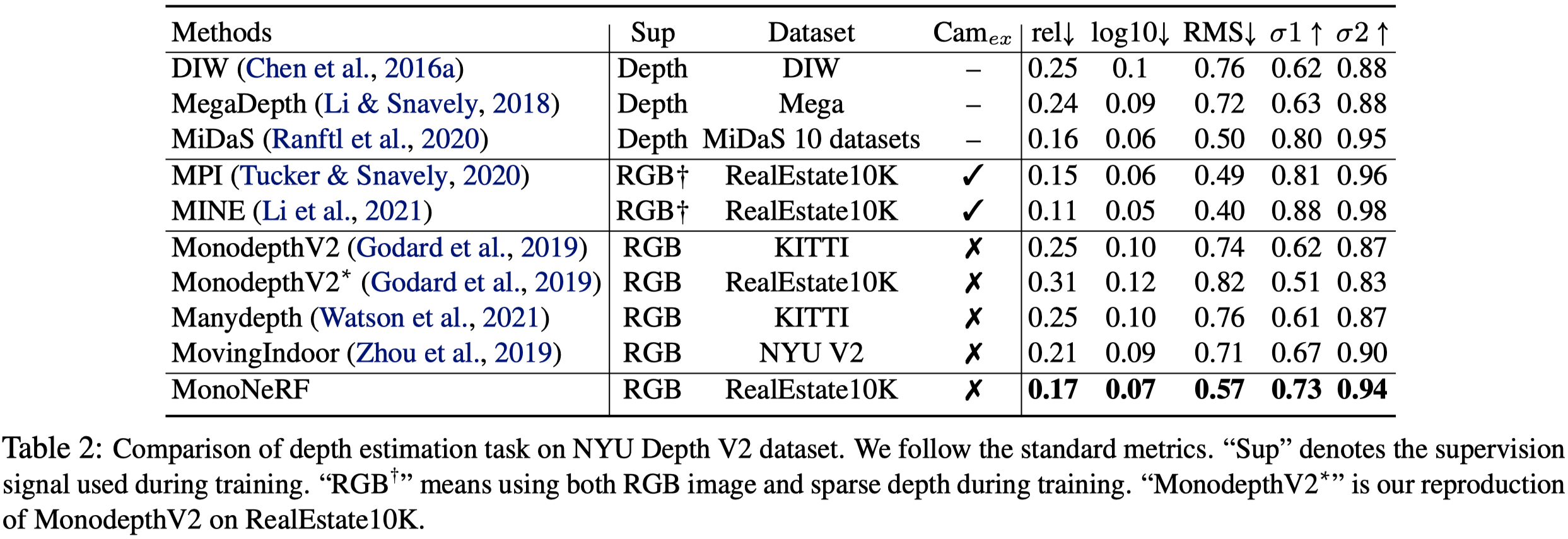
- 與 depth supervision 的方法相比,本篇方法取得可比較的效果。
- 因為 MINE 使用 camera pose,本篇效果比較差。
- 但優於其他沒有使用 depth supervision 的方法。
Camera Pose Estimation#
- Dataset
- RealEstate10K
- Metric
- Absolute Trajectory Error (ATE)
- Mean
- RMSE
- Max error
- Absolute Trajectory Error (ATE)
- Baseline
- SSV
- SfMLearner
- P$^2$Net
- COLMAP
- VideoAE

- 本篇方法明顯超越以往的方法。
- RMSE 減少 80%。
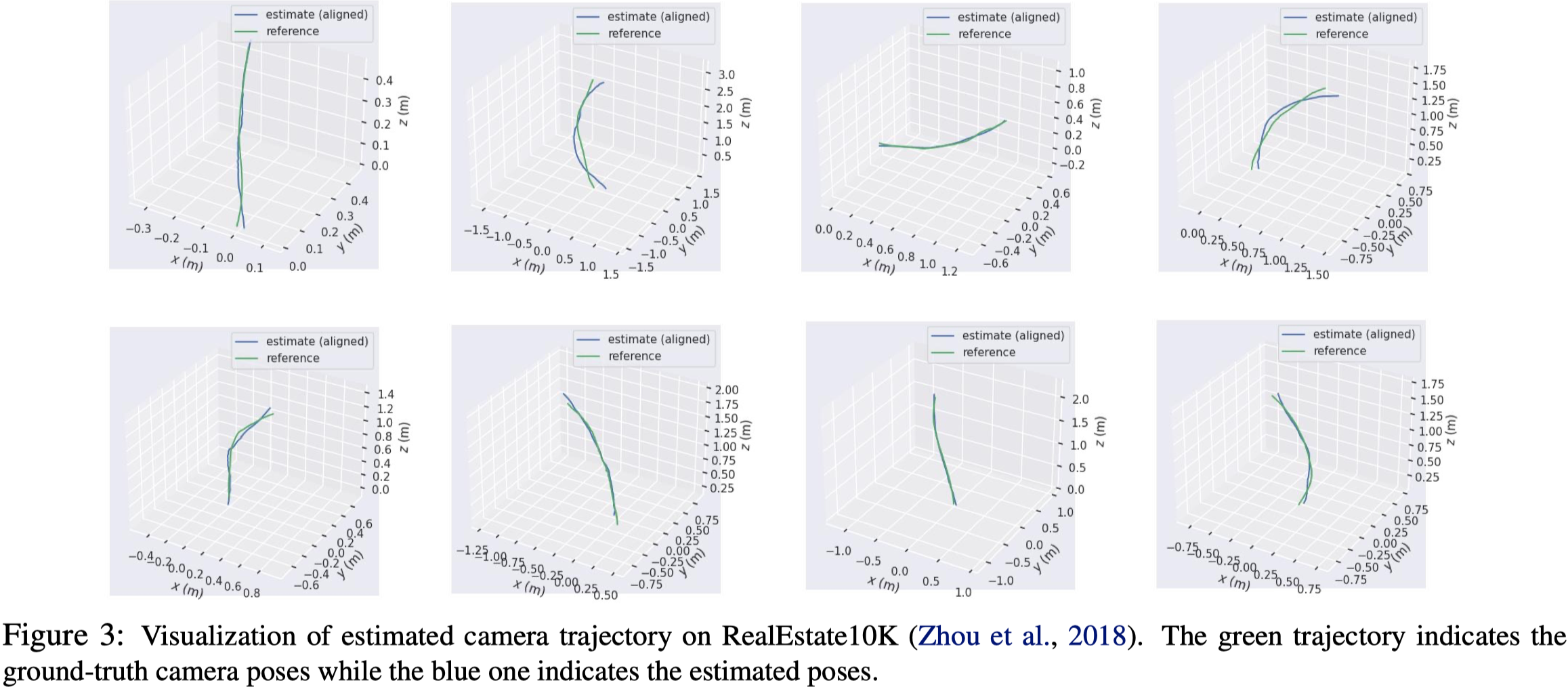
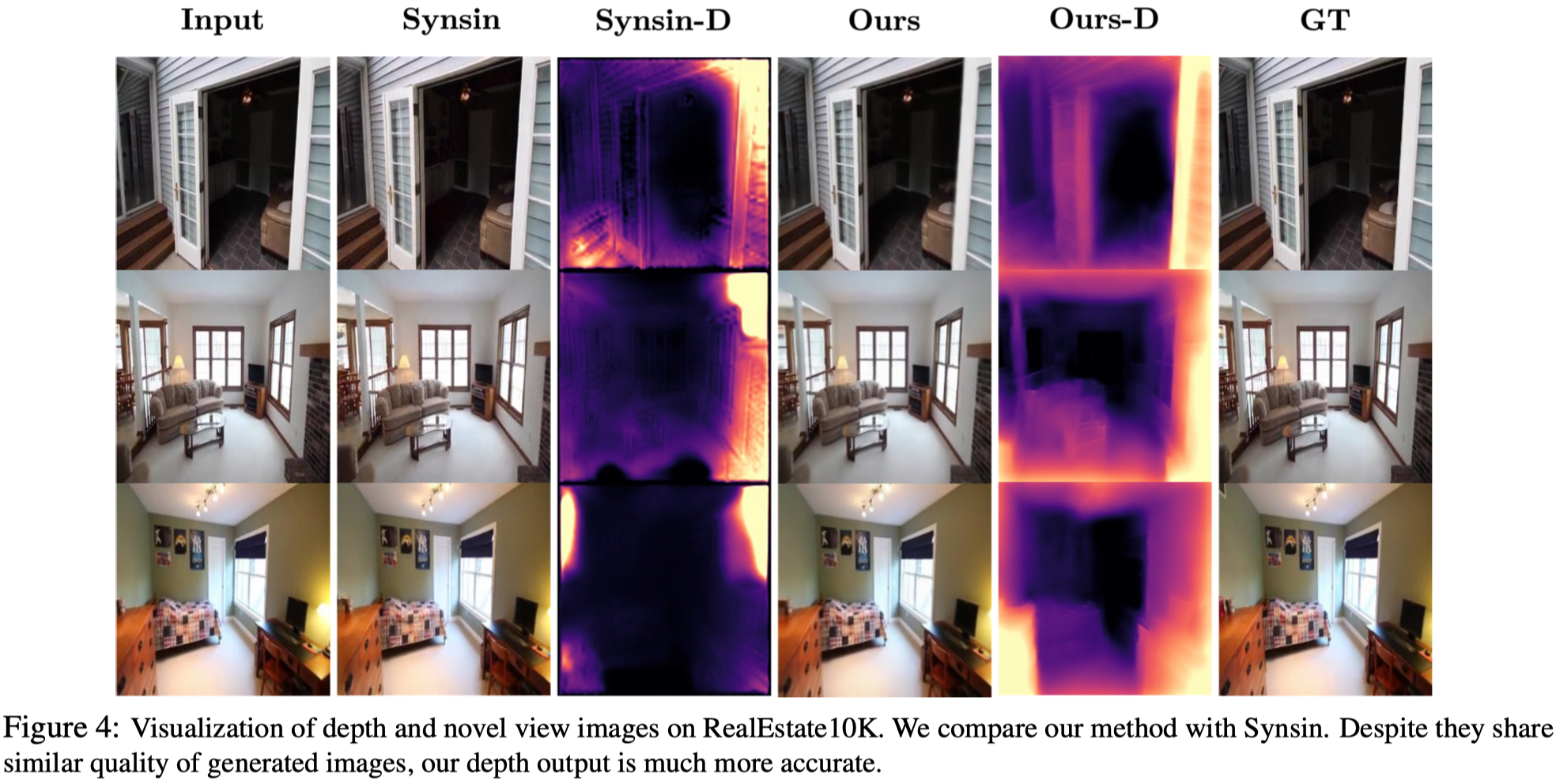
Novel View Synthesis#
- Dataset
- RealEstate10K
- Metrics
- PSNR
- SSIM
- Perceptual Similarity with VGG

- 如同 camera pose estimation,本篇方法可以獲得可比較或超越的結果。
- 對於有使用 camera pose 做監督的方法,本篇的方法會些微落後。
- 對於其他沒有使用 camera pose 的方法,本篇可以獲得更好的效果。

Ablation Study#
Autu Scale Calibration
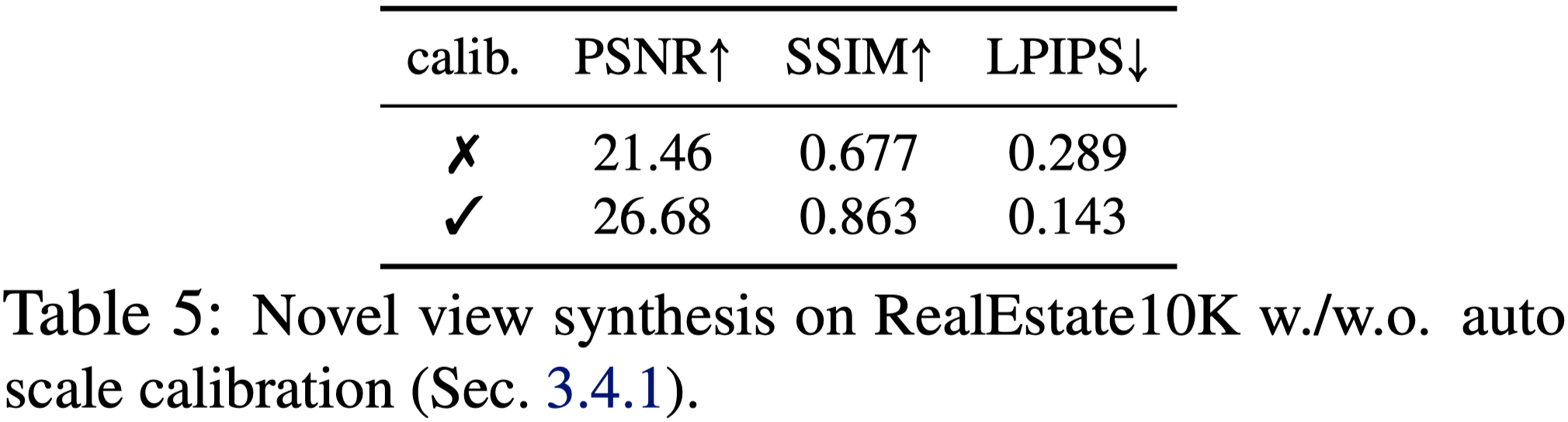
Number of Planes
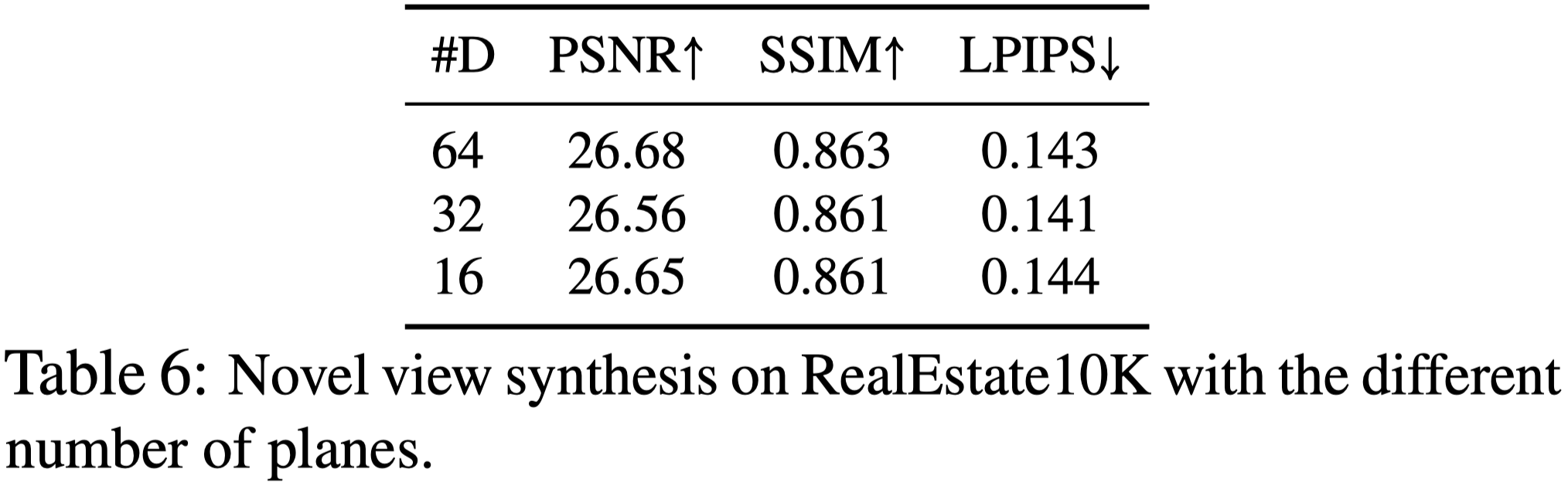
Amount of Training Data
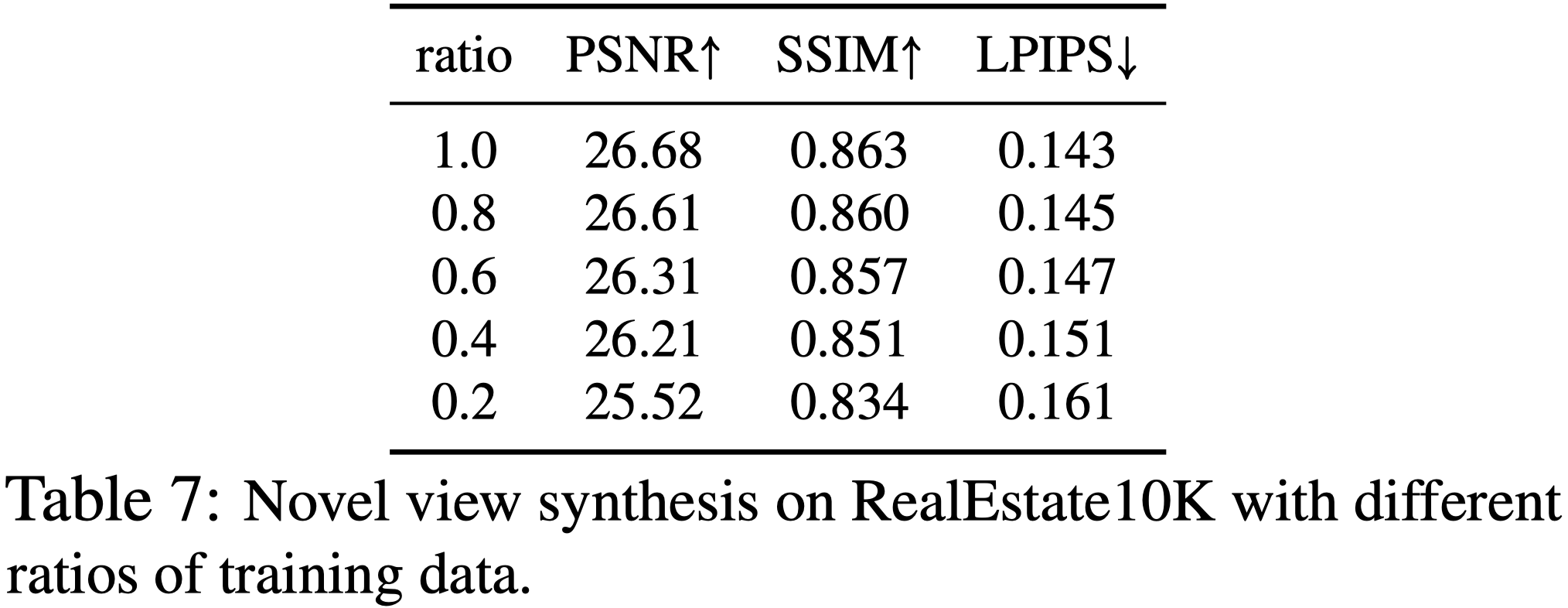
更多的 data 可以得到更好的效果。
Generalization Ability
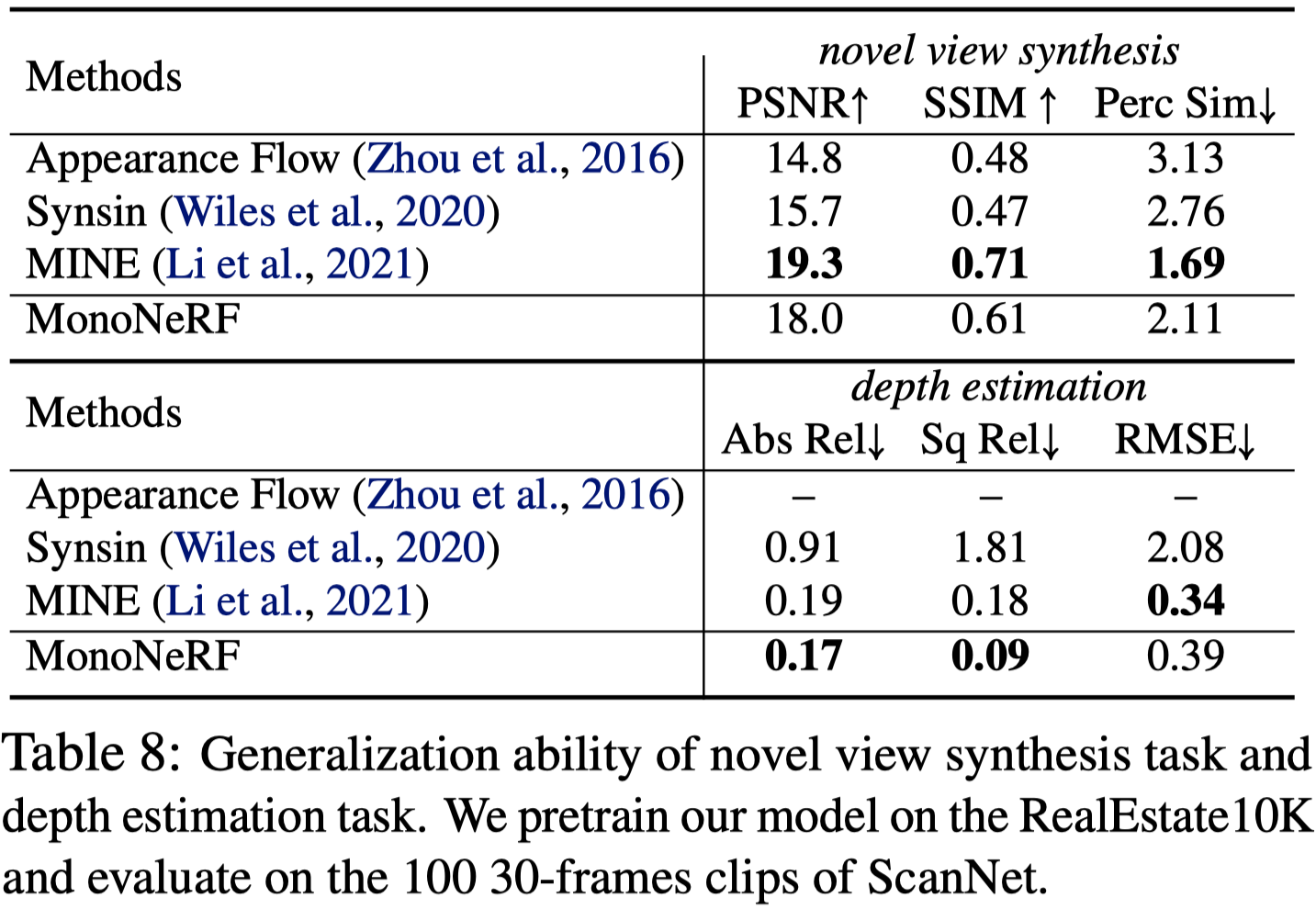
Pretrain 在 RealEstate10K,測試在 ScanNet。
Conclusion#
- 提出使用 autoencoder 架構來將影片解構成 camera motion 與 depth map。
- 使用 Multiplane NeRF 作為 decoder 來表示 3D 場景。
- 引入 auto-scale calibration strategy ,即使沒有相機姿態也可以學習解構表示。
- 本篇方法可以在 depth estimation, camera pose estimation 和 novel view synthesis 三個子任務中都取得不錯的表現。即使與其他使用 ground-truth camera pose 或 depth map 的方法相比,都能取得可比較甚至更好的結果。
